The DAX OR function in Power BI is used to perform a logical disjunction on two expressions. It returns TRUE if either of the expressions evaluates to TRUE, and FALSE only if both expressions are FALSE. This function is useful for combining multiple conditions where at least one condition must be met.
Syntax:
OR(<logical1>, <logical2>)
<logical1>: The first condition to evaluate.
<logical2>: The second condition to evaluate.
Purpose:
The OR function allows you to test multiple conditions and return TRUE if any one of the specified conditions is TRUE. This is essential for scenarios where you need to check if at least one of several criteria is satisfied.
Example:
Suppose you have a table named "Sales" with columns "Product", "Revenue", and "UnitsSold". You want to create a new column that flags sales as "High Priority" if the revenue is greater than 200 or the units sold are greater than 50.
You can use the OR function as follows:
HighPriority = IF(OR(Sales[Revenue] > 200, Sales[UnitsSold] > 50), "Yes", "No")
This formula creates a new column named "HighPriority" that assigns "Yes" if either condition is true, and "No" otherwise.
Example Scenario:
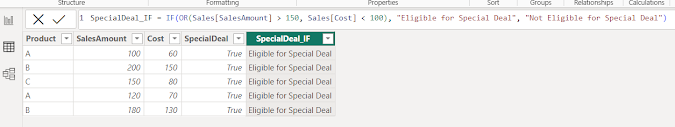
Consider the following "Sales" table with columns "Product", "SalesAmount", and "Cost":
Combining OR with IF Function
For a more meaningful result, we can combine the OR function with the IF function:
SpecialDeal_IF = IF(OR(Sales[SalesAmount] > 150, Sales[Cost] < 100), "Eligible for Special Deal", "Not Eligible for Special Deal")
In this example, rows where the sales amount is greater than 150 or the cost is less than 100 are labeled "Eligible for Special Deal". If both conditions are false, the row would be labeled "Not Eligible for Special Deal".


Comments
Post a Comment