The DAX UPPER function in Power BI is used to convert all characters in a text string to uppercase. This function is useful for standardizing text data, ensuring consistency in text values, and performing case-insensitive comparisons.
Purpose:
The UPPER function helps ensure that text data is consistently formatted in uppercase. This can be essential for tasks like data cleaning, preparing text for comparisons, and ensuring uniformity in text-based fields.
Example:
Suppose you have a table named "Customers" with a column "Name" that contains names in mixed case. You want to create a new column that shows all names in uppercase.
UppercaseName = UPPER(Customers[Name])
Example Scenario:
Assume you have the following "Customers" table:
You can use the UPPER function as follows:
Using the
UPPER function, you can convert all names to uppercase:UppercaseName = UPPER(Email[Email])
The resulting table would be:
Handling Edge Cases:
If the <text> is already in uppercase, the function returns the same text.
If the <text> contains non-alphabetic characters, they remain unchanged.
If the <text> is an empty string, UPPER returns an empty string.
UPPER function in Power BI is a straightforward but essential tool for text standardization and case-insensitive data handling. Understanding how to use the UPPER function effectively allows you to clean and prepare text data, ensuring consistency and reliability in your Power BI reports and analyses.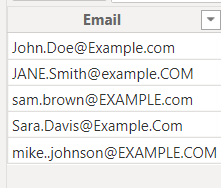

Comments
Post a Comment