Defining Functions
A function in Python is defined using the def keyword, followed by the function name, parentheses, and a colon. The code block within every function starts with an indentation and contains the function body.
Basic Function Definition
- function_name: The name of the function.
- parameters: Optional. Parameters that the function takes. They are also called arguments.
- Docstring: Optional. A string that describes what the function does.
- Function body: The block of code that performs the function’s task.
- return: Optional. Specifies what the function returns. If not specified, the function returns
Noneby default.
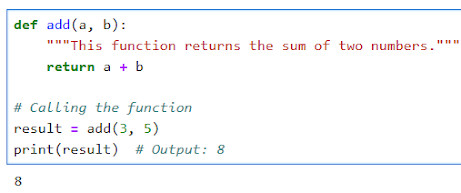
Example of Defining a Function
Calling Functions
A function is called by using its name followed by parentheses. If the function takes parameters, you pass the arguments inside the parentheses.
Basic Function Call
Examples of Defining and Calling Functions
Function with No Parameters
Function with Parameters
Function with Variable-Length Arguments
Sometimes, you might want to pass a variable number of arguments to a function. This can be achieved using *args for non-keyword arguments and **kwargs for keyword arguments.
def print_numbers(*args): """This function prints all the numbers passed to it.""" for num in args: print(num) # Calling the function print_numbers(1, 2, 3, 4) # Output: # 1 # 2 # 3 # 4
Return Statement
A function can return a value using the return statement. If a return statement is not used, the function returns None.
Function with a Return Value
Lambda Functions
For simple, small functions, you can use lambda functions (also known as anonymous functions).









Comments
Post a Comment