ODS stands for Operational Data Store. An ODS is a centralized database that provides a consistent, integrated snapshot of an organization's operational data from multiple source systems.
Unlike a data warehouse, which is optimized for analytical queries and historical reporting, an ODS is designed to support real-time or near-real-time operational processes and decision-making.
Here's an overview of the purpose and characteristics of a data warehouse ODS:
Integration Point
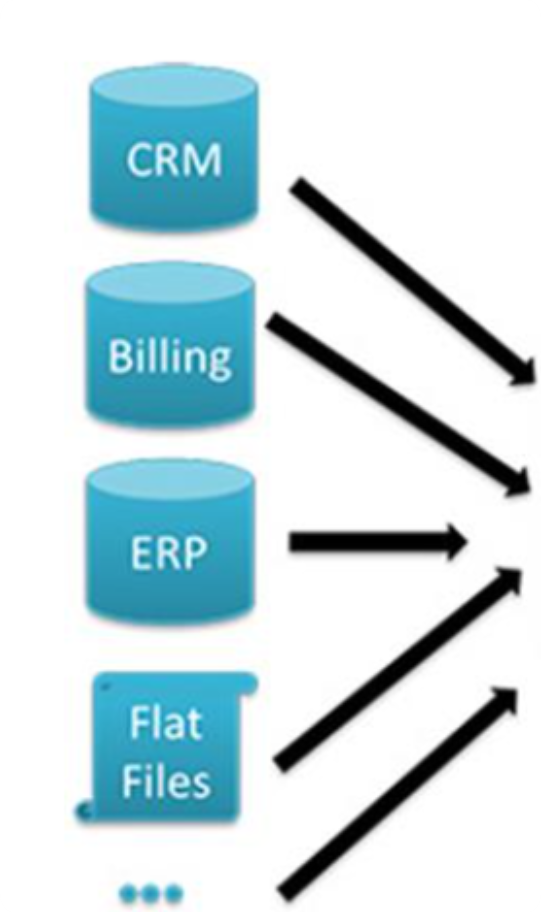
The ODS serves as an integration point for data from various operational systems within an organization, such as transaction processing systems, CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems, ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems, and others.
Real-Time or Near-Real-Time Data
While a traditional data warehouse typically loads data in batches at regular intervals (e.g., daily or weekly), an ODS often receives data in real-time or near-real-time. This ensures that users have access to the most current operational data for decision-making purposes.
Granular and Detailed Data
The ODS stores granular and detailed transactional data, providing a comprehensive view of business activities as they occur.
This level of detail enables organizations to track and analyze operational processes in depth.
Data Quality and Cleansing
Data quality and cleansing processes are essential components of an ODS.
Incoming data is often subjected to validation, cleansing, and standardization procedures to ensure accuracy, consistency, and completeness.
Data Transformation and Enrichment
The primary purpose of an ODS is to support operational processes and decision-making in real-time or near-real-time.
It provides a unified view of operational data, enabling organizations to monitor performance, detect issues, and make timely adjustments as needed.
Data Feeds to Data Warehouse
In many organizations, the ODS serves as a staging area for feeding data into the data warehouse.
After data is processed and cleansed in the ODS, it may be transformed further and loaded into the data warehouse for long-term storage and analysis.





Comments
Post a Comment