In Python, importing modules is a fundamental way to extend the functionality of your code by incorporating libraries and modules written by others. Here's a guide on how to import modules in Python:
Basic Import
To import a module, you use the import statement followed by the module name.
import math
Using Imported Functions
After importing, you can use the functions and variables defined in the module.
import math result = math.sqrt(16) # Use the sqrt function from the math module print(result) # Output: 4.0
Importing Specific Items
You can import specific functions, classes, or variables from a module using the from ... import ... syntax.
from math import sqrt, pi result = sqrt(16) print(result) # Output: 4.0 print(pi) # Output: 3.141592653589793
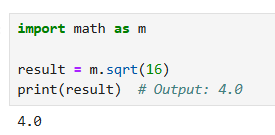
Renaming Modules
To avoid name conflicts or for convenience, you can rename modules using the as keyword.
import math as m result = m.sqrt(16) print(result) # Output: 4.0
Importing All Items
To import all functions and variables from a module, use the from ... import * syntax. However, this is generally discouraged because it can lead to unclear code and potential name conflicts.
from math import * result = sqrt(16) print(result) # Output: 4.0
Importing Submodules
Some modules have submodules which you can import separately.
import os.path path = os.path.join("folder", "file.txt") print(path) # Output: folder/file.txt
Checking Installed Modules
To see a list of installed modules, you can use the following:
help("modules")
Installing Modules
If you need to install a third-party module, you can use pip (Python's package installer).
pip install requests
Importing Installed Modules
Once installed, you can import third-party modules just like built-in ones.
import requests response = requests.get("https://www.example.com") print(response.text)
-----------
-----------
By understanding these basics, you can effectively manage and utilize modules in your Python projects.







Comments
Post a Comment