Python sets are a powerful data structure used to store an unordered collection of unique elements. They are particularly useful for membership testing, removing duplicates, and performing mathematical set operations like union, intersection, and difference.
Key Characteristics of Sets
- Unordered: The items in a set do not have a defined order.
- Unique Elements: A set automatically removes duplicate items.
- Mutable: Elements can be added or removed from a set.
- Heterogeneous: Elements of different types can coexist in a set.
Creating Sets
You can create a set using curly braces {} or the set() function.
# Using curly braces my_set = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} print(my_set) # Output: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} # Using the set() function my_set = set([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) print(my_set) # Output: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
Basic Set Operations
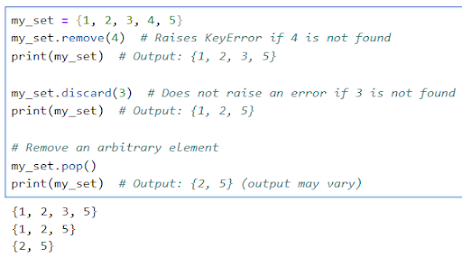
Adding Elements
Set Operations
Union
The union of two sets is a set containing all elements from both sets.
set1 = {1, 2, 3} set2 = {3, 4, 5} union_set = set1.union(set2) print(union_set) # Output: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} # Using the | operator union_set = set1 | set2 print(union_set) # Output: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
Intersection
The intersection of two sets is a set containing only the elements that are in both sets.
set1 = {1, 2, 3} set2 = {2, 3, 4} intersection_set = set1.intersection(set2) print(intersection_set) # Output: {2, 3} # Using the & operator intersection_set = set1 & set2 print(intersection_set) # Output: {2, 3}
Difference
The difference of two sets is a set containing elements that are in the first set but not in the second.
set1 = {1, 2, 3} set2 = {2, 3, 4} difference_set = set1.difference(set2) print(difference_set) # Output: {1} # Using the - operator difference_set = set1 - set2 print(difference_set) # Output: {1}
Symmetric Difference
The symmetric difference of two sets is a set containing elements that are in either set, but not in both.
set1 = {1, 2, 3} set2 = {2, 3, 4} symmetric_difference_set = set1.symmetric_difference(set2) print(symmetric_difference_set) # Output: {1, 4} # Using the ^ operator symmetric_difference_set = set1 ^ set2 print(symmetric_difference_set) # Output: {1, 4}
Other Useful Methods
- issubset(): Check if one set is a subset of another.
- issuperset(): Check if one set is a superset of another.
- copy(): Create a shallow copy of a set.







Comments
Post a Comment